In this section
In This Section
Note:
- For images that are labelled with AP or PA, this terminology refers to the direction of the X-rays passing through the body part, i.e. posteroanterior (PA) the x-rays enter from back to front, and for anteroposterior (AP) they're from front to back.
- All images should also contain anatomical markers to help identify orientation of the body parts and additional information related to the patient. This has been cropped on some of the images below for confidentiality.
CT | Neck
Sagittal bone window of the cervical spine, taken using Computed Tomography (CT).
.png)
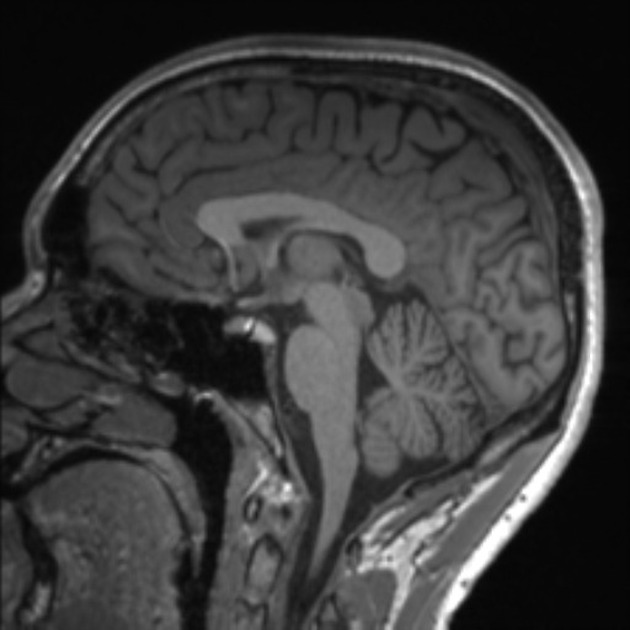
MRI | Brain
Sagittal T1 scan of the brain, taken using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
MRI | Knee
Sagittal T1 scan of the knee, taken using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
.jpeg)
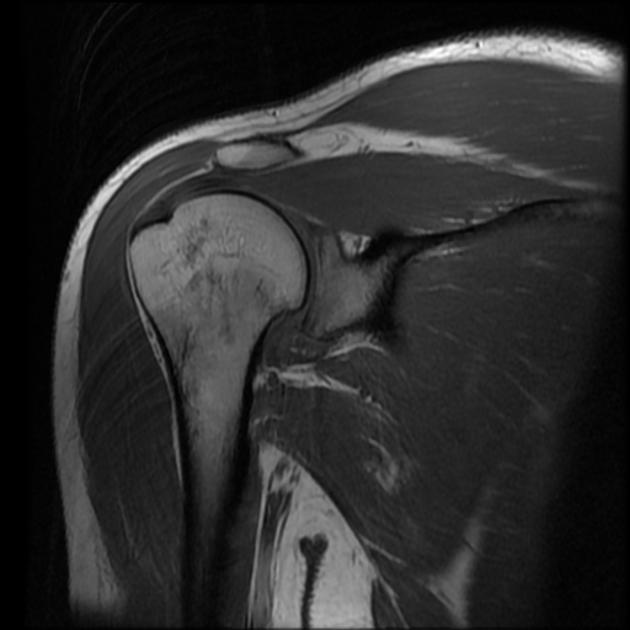
MRI | Shoulder
Coronal T1 of the shoulder, taken using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
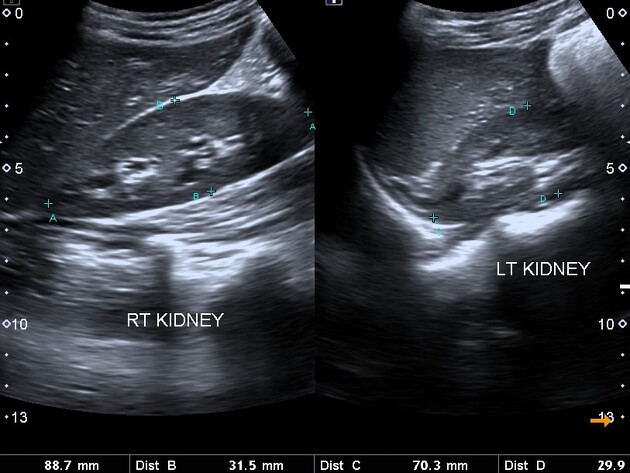
Ultrasound | Kidneys
Ultrasound scan showing the kidneys.
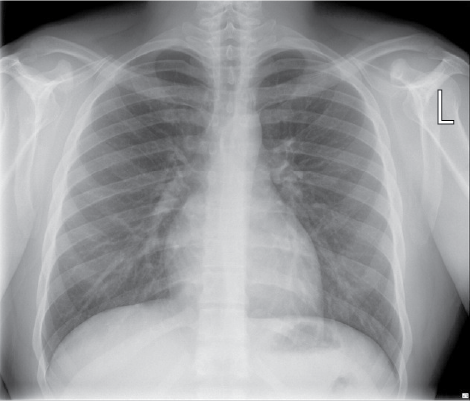
X-ray | Chest
Posteroanterior (PA) standing view of the chest, taken using X-ray.
X-ray | Foot
Anterior posterior (AP) projection X-ray of the foot.
.jpg)
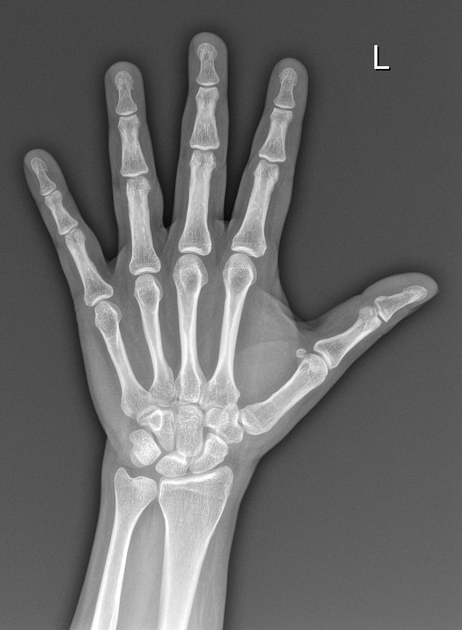
X-ray | Hand
Posteroanterior (PA) projection X-ray of the hand.